In the past, the storage space on computers was measured with Megabyte(MB), but is now measured by Terabyte (TB). Nowadays, most of us don’t take backups, and as a result, we’re losing our data. When we think of this for companies, losing data is a big problem. Owing to the RAID( redundant array of independent disks) structure you can gain performance or you can create security to prevent data loss.
RAID levels
Raid 0
- At least 2 discs are required.
- Provides performance
- Has no security.

Raid 1
- At least 2 discs are required.
- The same data is written on all disks, so data is safely protected.
- The capacity is limited to the minimum size of the disc.

Raid 2
- At least 14 disks are required.10 of them are used for data and 4 of them are used for ECC (Error Correction Control)
- Raid 2 is not used today because Raid cards contain ECC.

Raid 3
- Access is very fast.
- At least 3 discs are required.
- No data loss.
- Not used today.

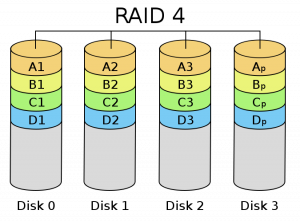
Raid 4
- It reads quickly during writing.
- Write speed is reduced.
- At least 3 disks are required.
Raid 5
- All disks have both parity information and data information.
- Data is written separated into pieces before being written to disk on the Raid cards.
- At least 3 disks are required.
- Is the most common used Raid level.

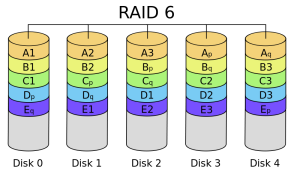
Raid 6
- The difference of Raid 6, which is almost the same as Raid 5, requires at least 4 disks and creates 2 separate parity disks.
- Writing speed is slower than Raid 5.
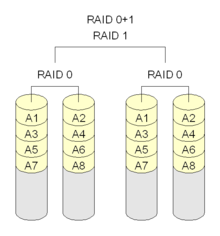
Raid 0+1
- It is a combined of Raid 0 and Raid 1
- Provides the best performance.
- At least 4 disks are required.
- It is the most preferred level.
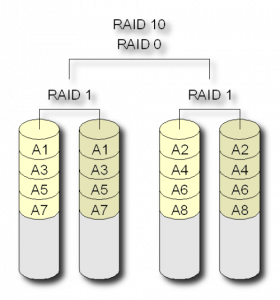
Raid 1+0
- It is the combination of two Raid 1 in Raid 0.
- At least 4 disks are required.
- Provides high performance.
Raid 1+5
- The safest level.
- It is the combined of three Raid 1 in Raid 5
- At least 6 disks are required.

Raid 5+0
- Provides high performance.
- Provides high security.
- It is the combination of two Raid 5 in Raid 0.





