If you have tampered with your hard disk and segmented it, you have often come across terms such as MBR and GPT. Especially users running Dual-Boot Mac are very familiar with these terms.
Users are aware that their hard drive can be partitioned. However, many of these users do not know how the operating system configures these partitions. This is where MBR (Master Boot Record) and GPT (Guild Partition Table) come into play. Despite the different architectures, both structures are used for information collection and management for partitions.
What is the Master Boot Record (MBR)
MBR is the system used to manage partitions but still used by many users today. Information about the partitions organized in the storage area is also kept by this system. MBR also contains code for scanning partitions for the operating system.
The MBR disk can have up to four primary partitions. You can set the fourth part to be expandable to create more partitions. In this way, you can create more sub-sections within the fourth section. Because MBR disks use a 32-bit recording system for partitions, each partition has a 2TB limit.

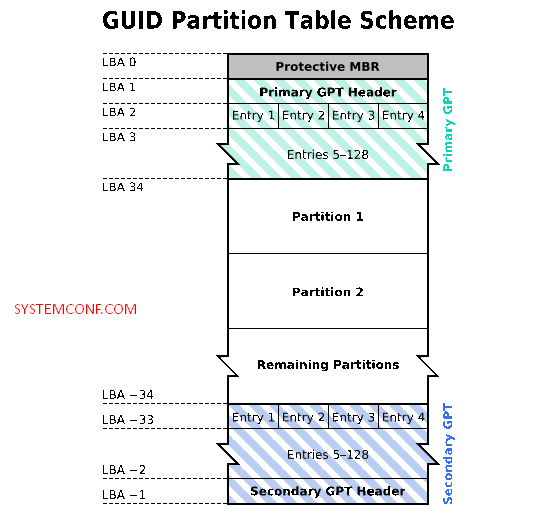
What is GUID Partition Table (GPT)
This system, which has the UEFI standard, is the most up-to-date system that organizes the partitions of the disk. If you have a UEFI-based system, GPT should be used instead of MBR. Unlike MBR, theoretically unlimited partitions can be created in GPT.
GPT is one step ahead of MBR as its storage area. It can reach 2TB limit for each part in MBR and 9.44ZB in GPT. Of course, this value is only theoretically possible. Because in Windows operating systems, the maximum capacity of each partition is fixed at 256TB.
GPT disks have two GPT Headers, first and last. One of the most important details that make GPT more useful than MBR is this sequence. Since GPT disks store the backup header at the end, it is much easier to recover the disk when the main header is damaged. GPT disks also use CRC32 (cyclic redundancy check) checks to detect problems.
Another noteworthy detail in the diagram, Protective MBR, enables BIOS-based systems to boot GPT disks with the bootloader in this area. In addition, Protective MBR prevents disk tools that are not defined against GPT from damaging the disk.
Operating System Support
Intel Macs use GPT on their disks as standard. It is not possible to install Mac OS X on the MBR system. Also, many Linux kernels have GPT support. Grub 2 bootloader must be used to use GPT disk with Linux.
On the Windows side, GPT disks have been supported since Windows XP. Computers with 64-bit Windows 8 (except 32-bit XP) use GPT by default, while MBR is the default in Windows 7 and earlier.
For many normal users, using an MBR or GPT disk will not make a difference. If the 2 TB limit per part is enough for you, MBR disks will do your job well. However, most computers have UEFI support, so these computers can only work with GPT.




