Sysmon (System Monitor) is one of its tools to monitor activities on Windows operating systems in detail. It provides detailed information on the created processes, network connections, file changes, registry activities. Sysmon activities can be viewed through the Windows Event Log. It can also be collected in SIEM or big data environments and can be used in cyber incident detection and threat hunting. In short, it is possible to create an Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR) infrastructure for Windows machines with Sysmon.
Sysmon logs
Sysmon logs can be accessed via the Windows Event Log from “Application and Services Logs” -> “Microsoft” -> “Windows” -> “Sysmon” -> “Operational”.

The latest version of Sysmon and events
The most current version of Sysmon is April 28, version 11.0 released in 2020. You can visit here to download and read the release notes. With the latest version, there are a total of 23 different events on Sysmon.
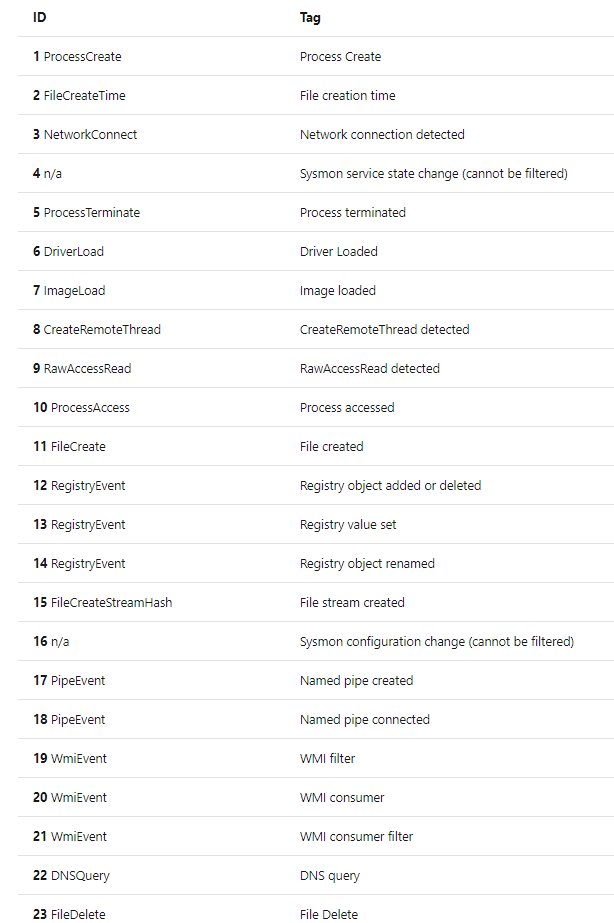
You can find Sysmon specific log samples in the web address below.
https://www.ultimatewindowssecurity.com/securitylog/encyclopedia/default.aspx
Sysmon Setup
It is installed using the Sysmon command line. There are also a few optional options during the installation phase. You can download the Sysmon application from the link below?
https://download.sysinternals.com/files/Sysmon.zip
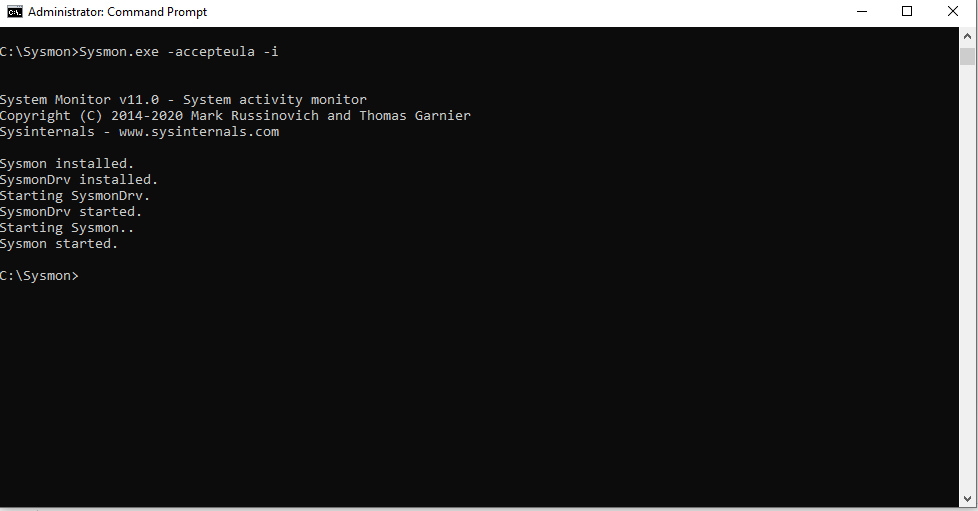
The following command is used to do the installation by default.
sysmon -accepteula –i
After the installation, the current configuration can be seen with the command below.
sysmon –c

Customization and Configuration
Logging details can be changed by creating a configuration file in XML format. For example, it is possible to select the hash algorithm as md5 and disable certain network connections. This will help us to achieve what we want to search for by saving from disk in the long term and by removing dirty information in the short term.
You can find a very detailed configuration file in the Github repos that I shared below and customize it to your own.
https://github.com/SwiftOnSecurity/sysmon-config
Sysmon Distribution and Scenarios with GPO
It is a sysmon sample configuration file with rules to register device drivers not associated with Windows or network connections only on TCP ports 80-443.

Sysmon Distribution with GPO
Sysmon rules and configuration settings are located in the registry in the following directory.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\ SYSTEM\ CurrentControlSet\ services\ SysmonDrv\ Parameters
You can distribute Sysmon rules across the organization using Group Policy Preferences (GPP). Once installed, the service queries the registry key for changes and is automatically updated and there is no need to restart.
Steps
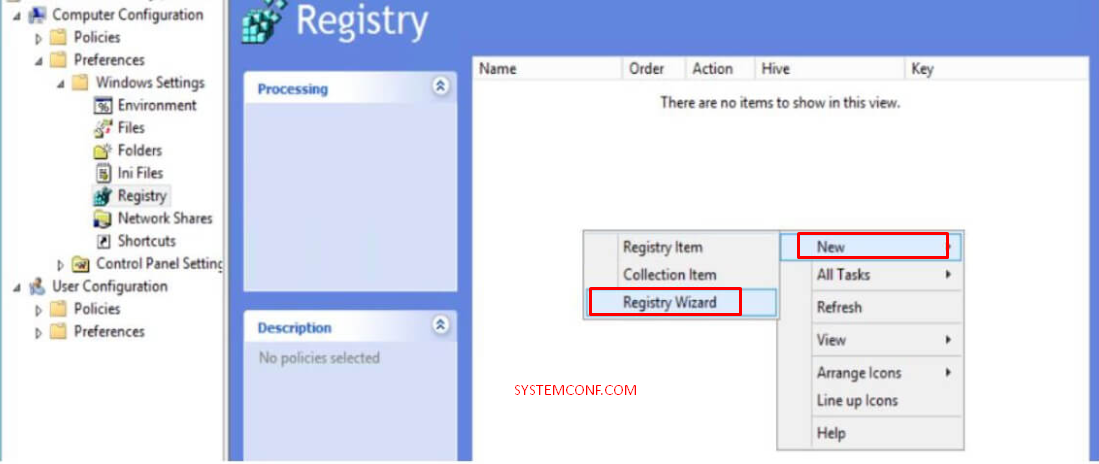
- Open the Group Policy Editor, go to the “Computer Configuration” section, then follow the path “Preferences,” Windows Settings and Registry “.
- Select Registry Wizard and click on “New”.
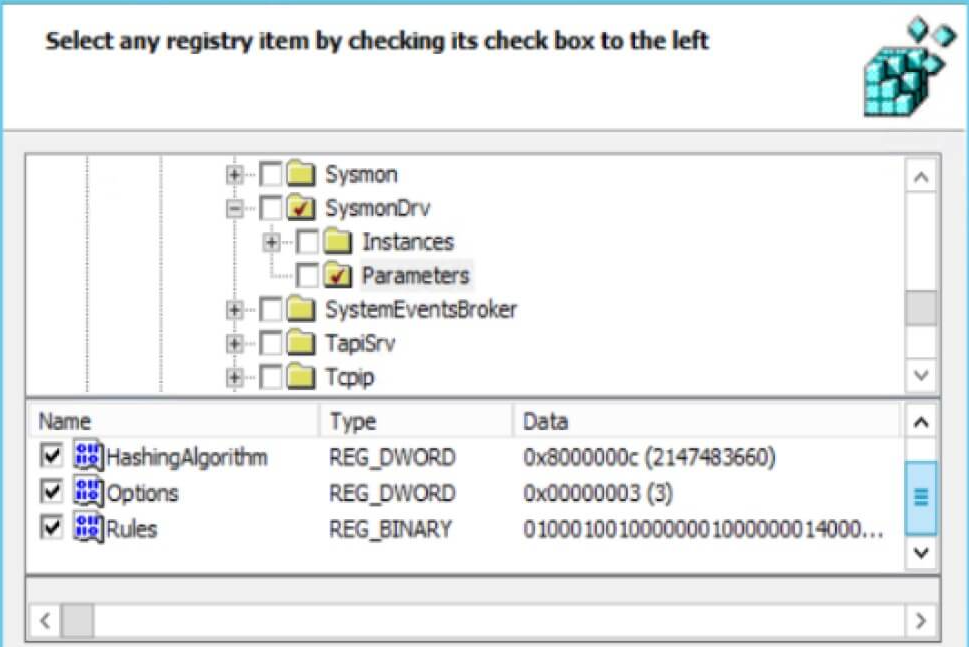
- Go to “HKLM \ SYSTEM \ CurrentControlSet \ Services \ SysmonDrv \ Parameters” and check “HashingAlgorithm, Options and Rules”.
- Deploy the GPO to the desired computers.
Sysmon Scenarios
- Determining the Queries for Gathering Information about the Domain.
- Detection of Program Assignments for Initialization from Suspicious Directories.
- Detecting Scheduled Task Additions.
- Detecting Vsadmin Uses.
- File Transfer Operations Using Bitsadmin.
- Detection of Pipe Names Used by Known APT Pests.
- Using Wscript or Cscript in Users’ Directories.
- Detection of Verclsid Use Used in Office Pests.
- Detecting File Execution From Suspicious Directories.
- Detecting calling cmd.exe with MMC
- Detecting Net.exe Calls.
- Detection of Powershell or CMD Calling with Wscript or Cscript.
- Detecting Backlinks from Suspicious Directories.
- Determining the Usage of Mimikatz.
- Detecting Shell Launch of Mstha.exe.
- Detecting Shell Launchings of Office Programs Using Macro.
- Detecting Shell Launchings of Office Programs.
- Detecting Access by Creating Thread to Lass.exe.
- Detecting Certutil.exe Use with Suspicious Parameters.
- Detecting Suspicious Parameters Using Cmd.exe and APPDATA.
- Detecting Calling Rundll32.exe by Control.exe.
- Detection of Driver Installation Attempts from Temp Directory.
- Detecting Access by Creating Thread to Lass.exe.
- Detecting File Downloads Using Powershell netclient.
- Detection of Access to Objectives Other Than Normal with Powershell Authorized User Account.
- Detecting Powershell Calls Using a Suspicious Parameter.
- Detection of Processes like Rundll32.exe to Communicate with Public IP Addresses.





