Security firm Secura published a technical article about CVE-2020-1472, an authentication vulnerability in Microsoft’s Netlogon authentication process, and the vulnerability was named “Zerologon.” The vulnerability that affects Windows servers allows unauthorized code to run on Microsoft Domain Controllers. The vulnerability, partially patched by Microsoft in the Tuesday release of August 14, 2020, exploits a weak cryptographic algorithm used in the authentication process of the Netlogon protocol.
Zerologon Vulnerability;
- To attackers manipulating Netlogon authentication procedures.
- To manipulate the domain server by impersonating the identity of any computer on the network.
- Netlogon disables security features in the authentication process.
- It allows the domain controller to change the password of a computer on Active Directory.
The reason the vulnerability is called Zerologon is that the attack is done by adding a zero (0) character to certain Netlogon authentication parameters.
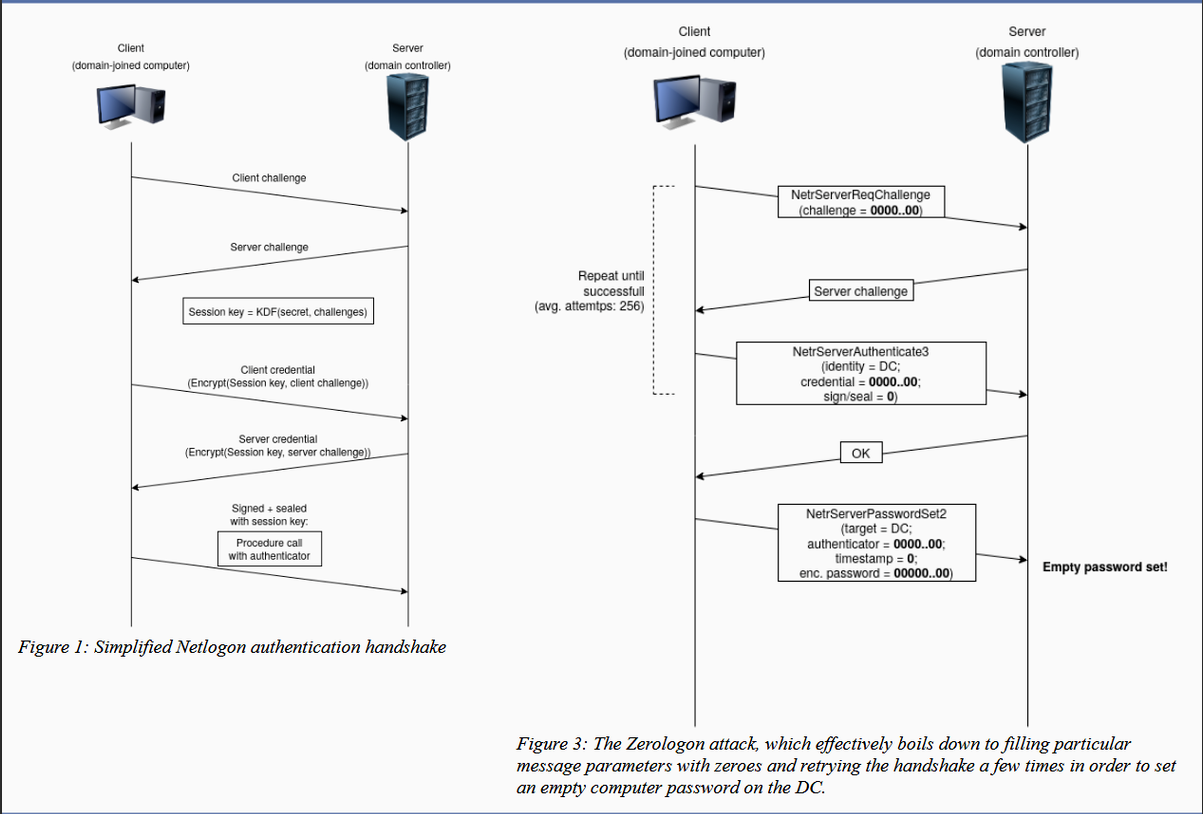
The reason the vulnerability is called Zerologon is that the attack is done by adding a zero (0) character to certain Netlogon authentication parameters.
The attack is fast and lasts up to three seconds. In addition, attackers can perform the Zerologon attack in many different scenarios. For example, an attacker could pretend to have the domain controller change its password and take over the entire corporate network. The attack can be used by threat actors to maintain persistence on the system by distributing malware on the target network. Or cyber kidnapping can be done by distributing ransomware. The only limitation on how to execute a Zerologon attack is that the attacker must have access to the target network.
ZeroLogon Proof of Concept + Exploit
Secura researchers have published a Python code that uses the Impact library to test for Zerologon vulnerability. The script tries to perform the Netlogon authentication bypass, and when it successfully handles the bypass, it will terminate and will not perform any Netlogon operations. When patching a domain controller, the detection script will give up after sending 2000 duplicate RPC calls and conclude that the target is not vulnerable.
Several PoC (+ exploits) of vulnerabilities that have received great attention in the cybersecurity community has been published on Github.





