ABBYY FineReader is a program that enables scanning and digitizing of scanned or paper files and/or documents, comparing different files with each other and making changes to PDF files. We will introduce FineReader, which offers different solutions to users for both professional and home use, by making an introduction to the program in this guide, and introducing its interface and general settings.
ABBYY FineReader Installation
You can download the application from the website below before starting the installation.
https://www.abbyy.com/download/
We are running the “ABBYY_FineReader_14_Trial” application that we downloaded.

On the “Winrar self-extracting archive” screen, we determine the location of the “Destination folder” from the “Browse” tab and click the “Install” button.

When we click the “Install” button, Winrar extracts the file to the location we specified.

On the “Choose setup language” page, we select the language in which the application will be installed and then click the “OK” button.
On the “License Agreement” page, we accept the license tab and click the “Next” button.

On the “Setup Type” page, we mark “Typical” and click the “Next” button.
On the “Ready to Install the Program” page, we start the installation by marking the tabs we want and clicking the “Install” button.
On the “Installing ABBYY FineReader 14” page, we are waiting a bit, as the installation will take a few minutes.
After the installation is finished, we mark the “Run ABBYY FineReader 14 on exit” tab to open the program and click the “Finish” button.
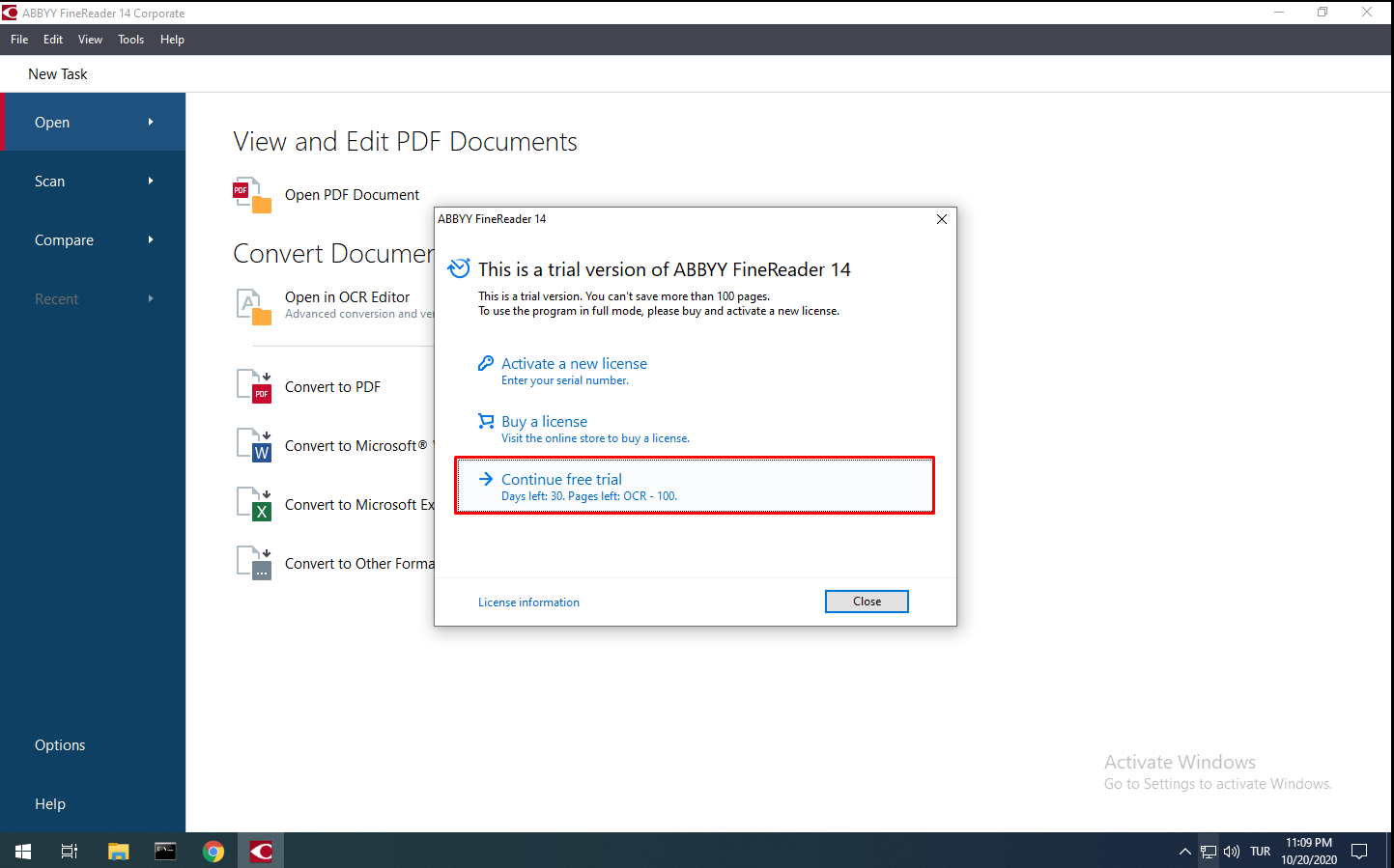
On the page that appears after the ABBYY FineReader 14 program starts, if you have a license, you can enter the license and activate the program. If not, you can mark the 30-day trial version.
ABBYY FineReader’s Interface
When you run ABBYY FineReader, you will see a screen like the one below. You can see the main menu options on the left. There are 4 different sections in this menu.

Open: With this command, you can open PDF files on your computer. In addition to this feature, you can convert files to different formats with the Convert option.
Scan: By choosing this command, you can scan with the scanner connected to your computer. You can also choose which file format you want it converted to while performing your scans.
Compare: With this command, you can compare different variations of the same file. If changes have been made to the file, you can see the differences between the two files using this tool.
Recent: You can quickly access the files you have recently opened from the Recent section.
FineReader’s General Settings
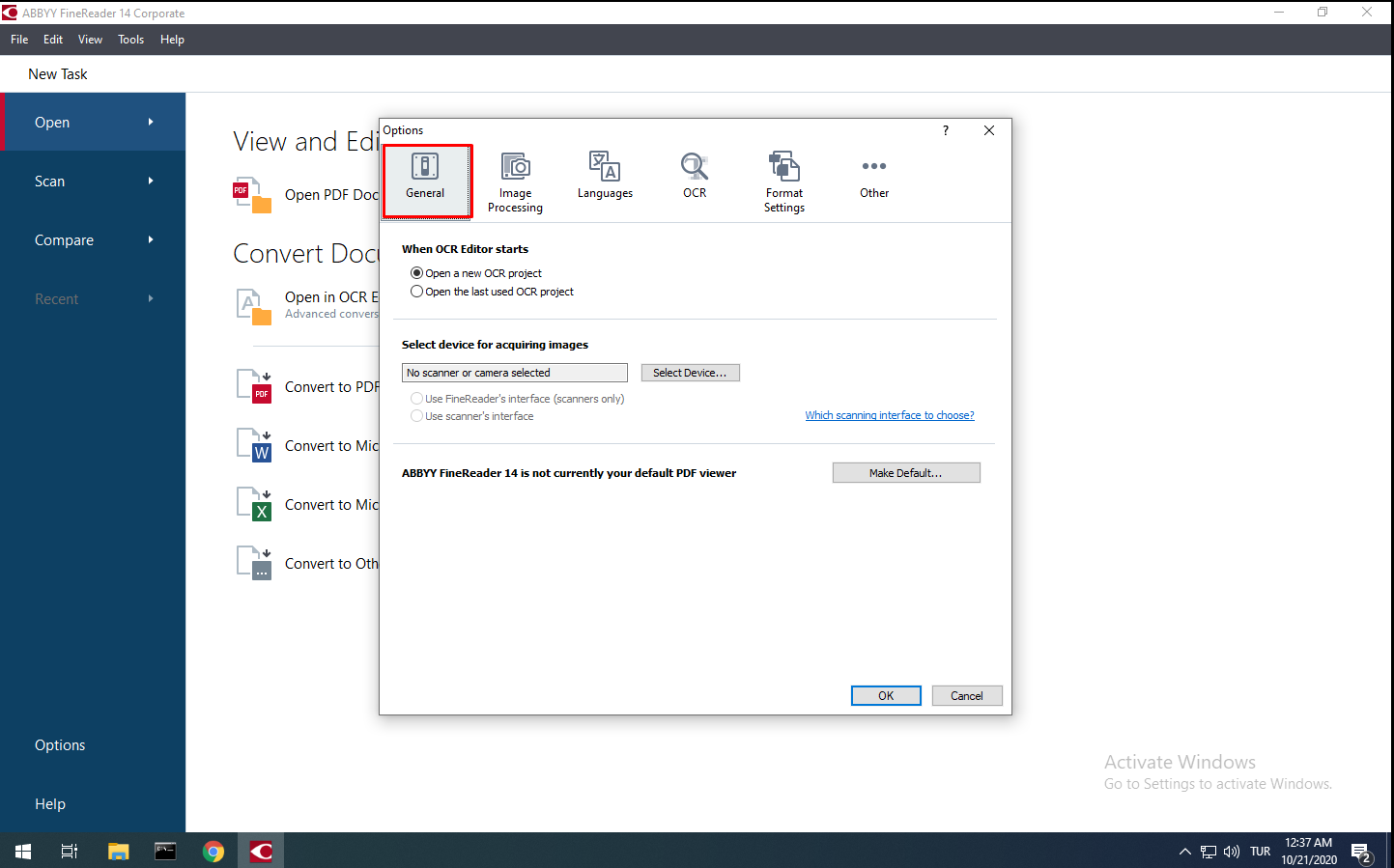
You can change FineReader’s standard settings. To do this, select the “Options” command at the bottom of the left pane. After selecting it, the Options window appears. In this window, you will see 6 different tabs as “General”, “Image Processing”, “Languages”, “OCR”, “Format Settings” and “Others”.

“General” Tab
In the “General” tab, you can specify how to make a selection when opening the OCR (Optical Character Recognition) Editor. At the bottom, you will see the browser options connected to your computer.
“Image Processing” Tab
On the “Image Processing” tab, we can choose whether the background recognition operations on the PDF editor are on or off. You can add files automatically to the OCR editor to determine whether they are processed and edit the image processing options.

“Languages” Tab
You can specify your standard language options by editing the OCR language options in the “Languages” tab.

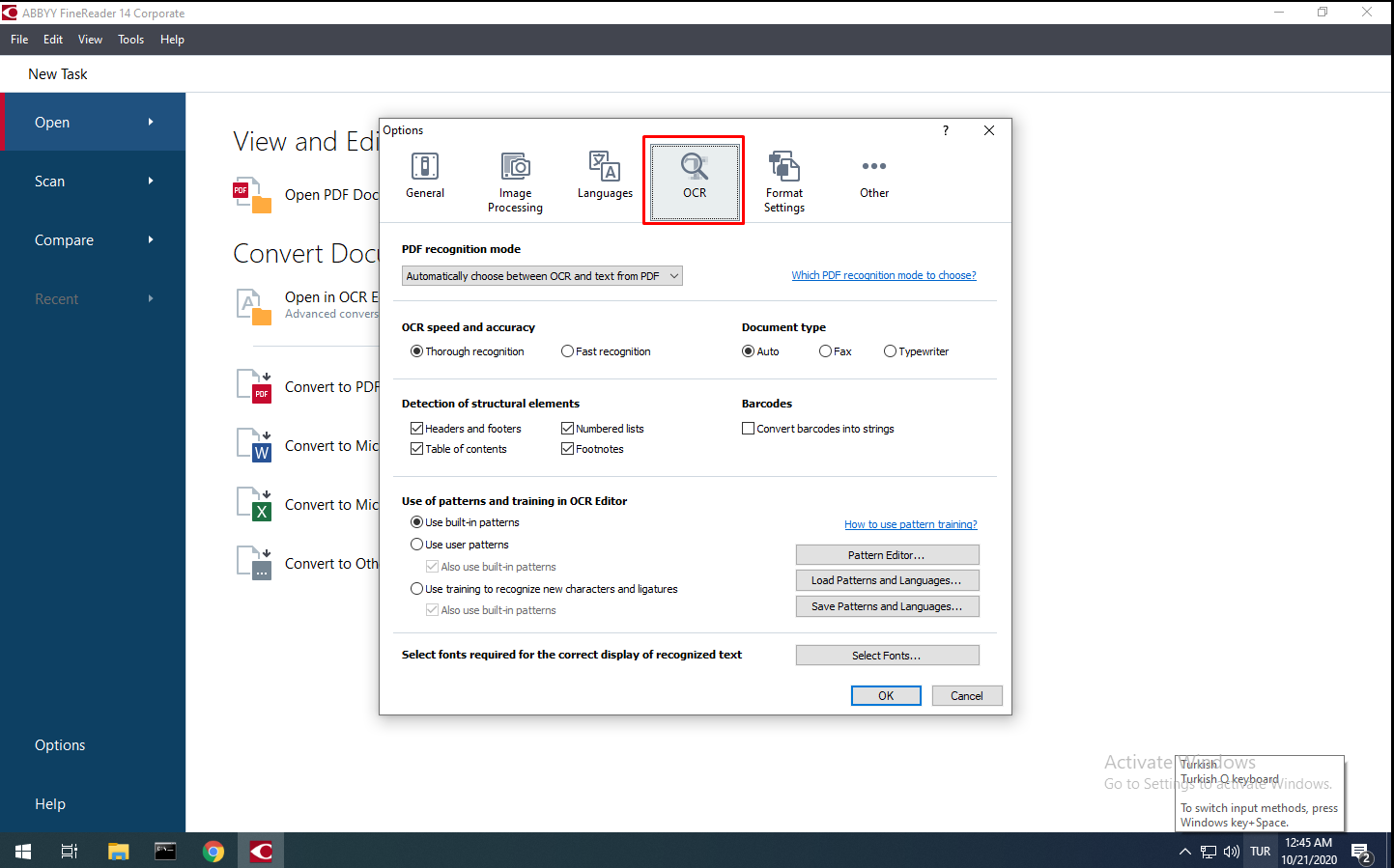
“OCR” Tab
In the “OCR” tab, you can access many different settings for optical character recognition. From this section, you can find settings such as how detailed the files will be processed, which format will be automatically converted, which elements will be recognized, and what kind of templates will be used.
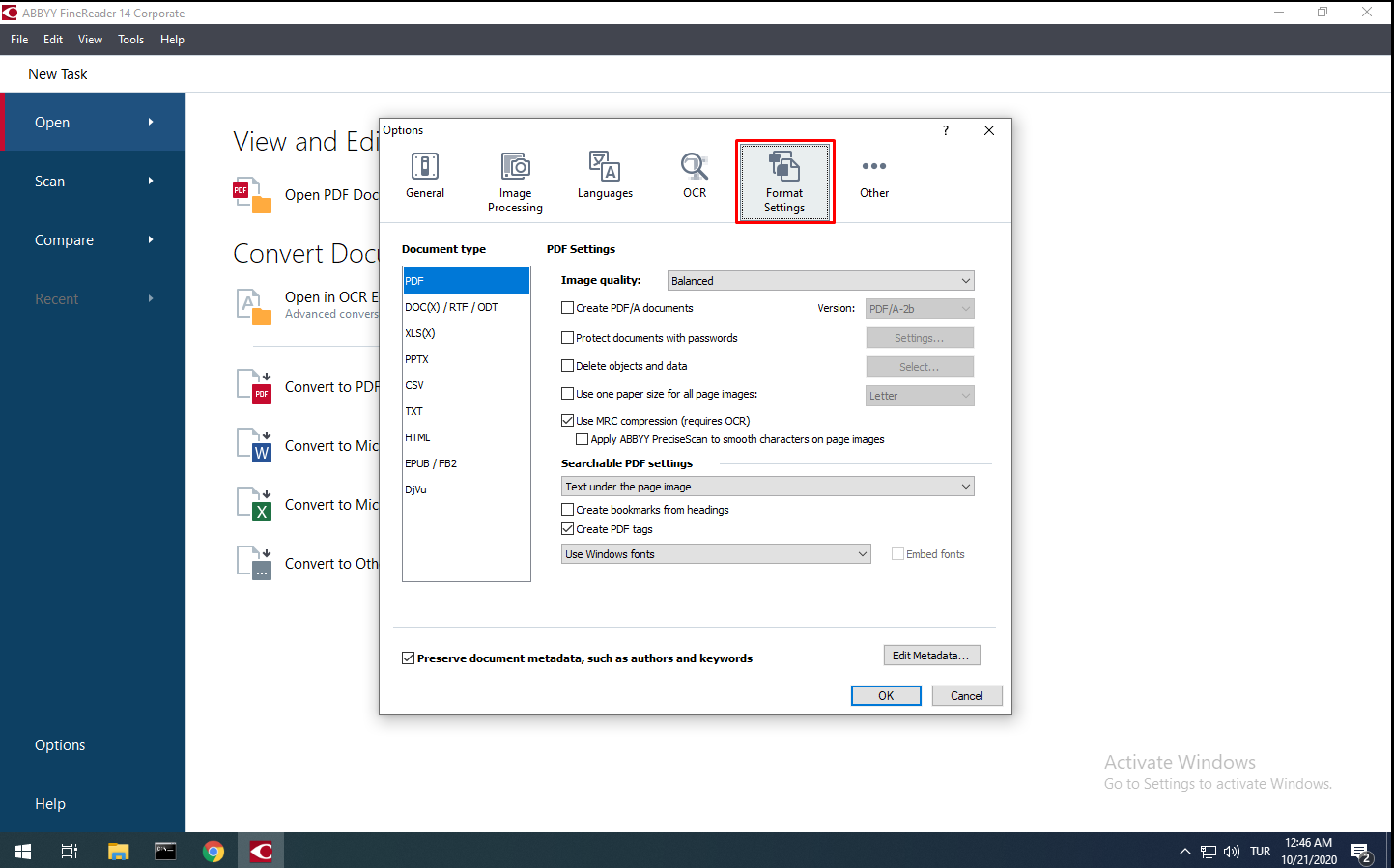
“Format Settings” Tab
In the “Format Settings” tab, you can make your own settings by editing the formats supported by FineReader, image quality, searchable PDF options and font options.
“Other” Tab
There are other settings in the “Other” tab. These include interface usage language, processor usage limits in OCR usage, automatic update settings.





