It is the advanced version of the ping command. Only ICMP is supported in ping, hping3 also supports protocols such as TCP, UDP, Raw-IP. The package is created according to the desired criteria and sent to the target IP. Thus, network tests or attacks can be done. Hping3 application comes installed on Kali Linux. It is a security application that can be installed on other Linux systems. Using this application, more firewalls, ips and Anti-DDoS devices are tested. The application generally aims to fill the session limits of the devices used to protect the target system by IP spoofing and to render the service inoperable.
Installing hping3
Depending on the operating system, you can install hping3 on your system using one of the following options.
Ubuntu, Kali and Debian
You can use the command below when installing on Ubuntu, Kali and Debian.
sudo apt-get install hping3
Fedora and Centos
You can also use the following command when installing on Fedora and Centos.
sudo yum install hping3
Major hping3 Parameters
-S: send syn (SYNchronize) packet
-p: destination port number
-c: number of packets to send
-d: the size of data to be sent
For other parameters and detailed usage, You can get information with hping3 –help or hping3 –h command.
root@omer:~# hping3 -h
usage: hping3 host [options]
-h --help show this help
-v --version show version
-c --count packet count
-i --interval wait (uX for X microseconds, for example -i u1000)
--fast alias for -i u10000 (10 packets for second)
--faster alias for -i u1000 (100 packets for second)
--flood sent packets as fast as possible. Don't show replies.
-n --numeric numeric output
-q --quiet quiet
-I --interface interface name (otherwise default routing interface)
-V --verbose verbose mode
-D --debug debugging info
-z --bind bind ctrl+z to ttl (default to dst port)
-Z --unbind unbind ctrl+z
--beep beep for every matching packet received
Mode
default mode TCP
-0 --rawip RAW IP mode
-1 --icmp ICMP mode
-2 --udp UDP mode
-8 --scan SCAN mode.
Example: hping --scan 1-30,70-90 -S www.target.host
-9 --listen listen mode
IP
-a --spoof spoof source address
--rand-dest random destionation address mode. see the man.
--rand-source random source address mode. see the man.
-t --ttl ttl (default 64)
-N --id id (default random)
-W --winid use win* id byte ordering
-r --rel relativize id field (to estimate host traffic)
-f --frag split packets in more frag. (may pass weak acl)
-x --morefrag set more fragments flag
-y --dontfrag set don't fragment flag
-g --fragoff set the fragment offset
-m --mtu set virtual mtu, implies --frag if packet size > mtu
-o --tos type of service (default 0x00), try --tos help
-G --rroute includes RECORD_ROUTE option and display the route buffer
--lsrr loose source routing and record route
--ssrr strict source routing and record route
-H --ipproto set the IP protocol field, only in RAW IP mode
ICMP
-C --icmptype icmp type (default echo request)
-K --icmpcode icmp code (default 0)
--force-icmp send all icmp types (default send only supported types)
--icmp-gw set gateway address for ICMP redirect (default 0.0.0.0)
--icmp-ts Alias for --icmp --icmptype 13 (ICMP timestamp)
--icmp-addr Alias for --icmp --icmptype 17 (ICMP address subnet mask)
--icmp-help display help for others icmp options
UDP/TCP
-s --baseport base source port (default random)
-p --destport [+][+]<port> destination port(default 0) ctrl+z inc/dec
-k --keep keep still source port
-w --win winsize (default 64)
-O --tcpoff set fake tcp data offset (instead of tcphdrlen / 4)
-Q --seqnum shows only tcp sequence number
-b --badcksum (try to) send packets with a bad IP checksum
many systems will fix the IP checksum sending the packet
so you'll get bad UDP/TCP checksum instead.
-M --setseq set TCP sequence number
-L --setack set TCP ack
-F --fin set FIN flag
-S --syn set SYN flag
-R --rst set RST flag
-P --push set PUSH flag
-A --ack set ACK flag
-U --urg set URG flag
-X --xmas set X unused flag (0x40)
-Y --ymas set Y unused flag (0x80)
--tcpexitcode use last tcp->th_flags as exit code
--tcp-mss enable the TCP MSS option with the given value
--tcp-timestamp enable the TCP timestamp option to guess the HZ/uptime
Common
-d --data data size (default is 0)
-E --file data from file
-e --sign add 'signature'
-j --dump dump packets in hex
-J --print dump printable characters
-B --safe enable 'safe' protocol
-u --end tell you when --file reached EOF and prevent rewind
-T --traceroute traceroute mode (implies --bind and --ttl 1)
--tr-stop Exit when receive the first not ICMP in traceroute mode
--tr-keep-ttl Keep the source TTL fixed, useful to monitor just one hop
--tr-no-rtt Don't calculate/show RTT information in traceroute mode
ARS packet description (new, unstable)
--apd-send Send the packet described with APD (see docs/APD.txt)

man hping3
After the installation is completed without any problem, you can find a document that tells us what we can do with hping3 with the man hping3 command.
root@omer:~# man hping3
Package sending with Hping
With the first packet sent with hping, TCP packet exchange is initiated. You can check this inter-flag shopping from that port with the tcpdump program.
Some TCP flags
SYN packet (hping3 -S): It is a TCP connection request. The first connection is initiated with this package.
ACK packet (hping3 -A): Replies to incoming packet request with this packet.
RST packet (hping3 -R): Resets the connection.
FIN packet (hping3 -F): Terminates the connection.
“SYN / ACK” package: The SYN \ ACK packet is sent in response to the incoming SYN packet to establish a connection.
“FIN” / ACK packet: This packet is sent to the sent FIN packet and the mutual session is terminated.
“RST” / ACK packet: The RST packet is sent to reset the mutual session on the RST packet sent to the destination.
Push packet (hping3 -P): Provides the progress of the plugged packets.
URG packet (hping3 -U): The packet is transmitted by prioritizing the priority order without waiting to reach the destination.
Hping3 Parameters with Example
hping3 –c: Specifies how many packets will be sent.
root@omer:~# hping3 -c 4 192.168.254.130 HPING 192.168.254.130 (eth0 192.168.254.130): NO FLAGS are set, 40 headers + 0 data bytes len=46 ip=192.168.254.130 ttl=64 DF id=0 sport=0 flags=RA seq=0 win=0 rtt=7.5 ms len=46 ip=192.168.254.130 ttl=64 DF id=0 sport=0 flags=RA seq=1 win=0 rtt=3.7 ms len=46 ip=192.168.254.130 ttl=64 DF id=0 sport=0 flags=RA seq=2 win=0 rtt=7.2 ms len=46 ip=192.168.254.130 ttl=64 DF id=0 sport=0 flags=RA seq=3 win=0 rtt=7.6 ms --- 192.168.254.130 hping statistic --- 4 packets transmitted, 4 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 3.7/6.5/7.6 ms

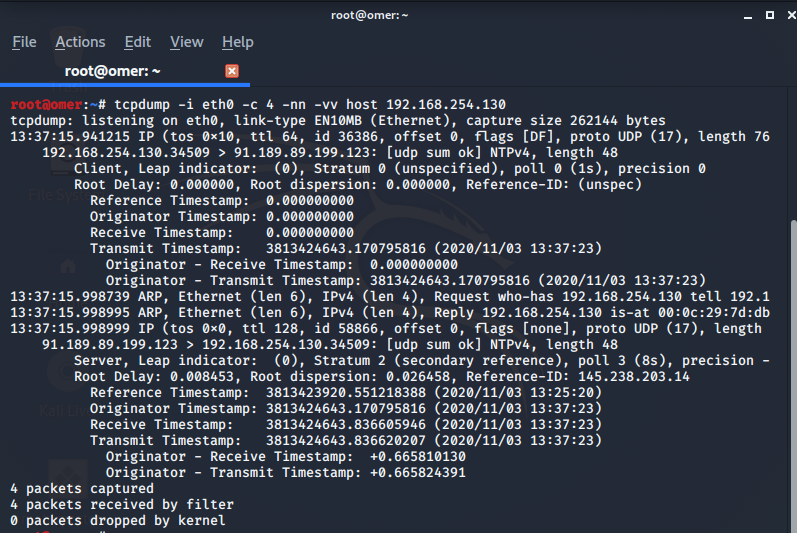
hping3 –icmp: execute a ping scan by running the icmp echo-request command. It takes the ICMP code (-K) and ICMP type (-C) values. Port scanning does not occur.

The output of the packages with the tcpdump command is as follows.
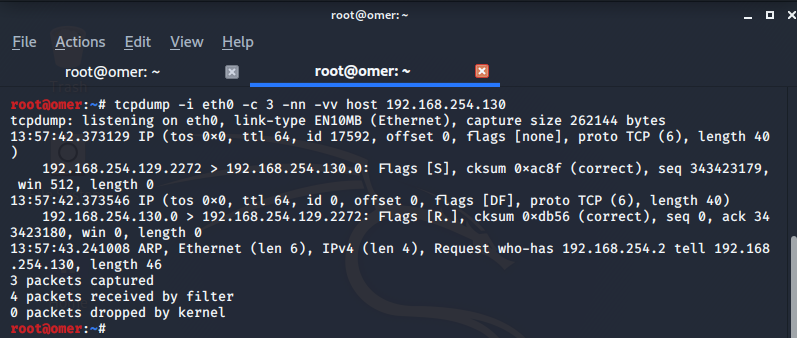
root@omer:~# tcpdump -i eth0 -c 4 -nn -vv host 192.168.254.130
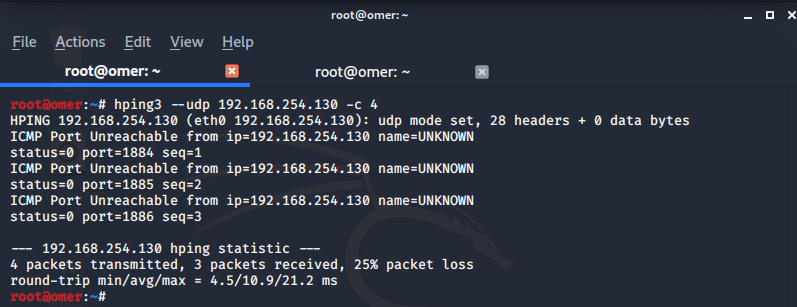
hping3 –udp: No data transmission with flags. ICMP packets are transferred.
root@omer:~# hping3 --udp 192.168.254.130 -c 4 HPING 192.168.254.130 (eth0 192.168.254.130): udp mode set, 28 headers + 0 data bytes ICMP Port Unreachable from ip=192.168.254.130 name=UNKNOWN status=0 port=1884 seq=1 ICMP Port Unreachable from ip=192.168.254.130 name=UNKNOWN status=0 port=1885 seq=2 ICMP Port Unreachable from ip=192.168.254.130 name=UNKNOWN status=0 port=1886 seq=3 --- 192.168.254.130 hping statistic --- 4 packets transmitted, 3 packets received, 25% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 4.5/10.9/21.2 ms
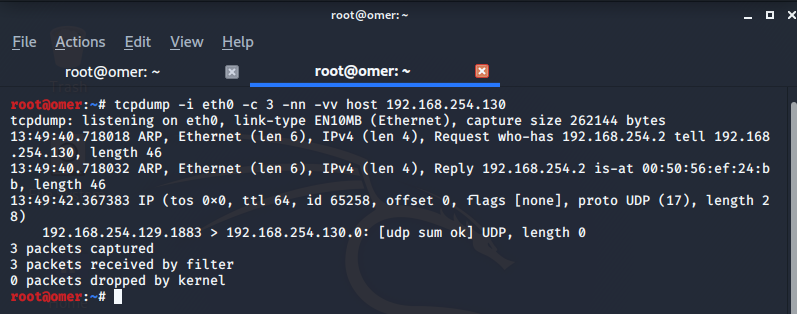
The output of the packages with the tcpdump command is as follows.
root@omer:~# tcpdump -i eth0 -c 3 -nn -vv host 192.168.254.130
hping3 -S: Which ports are used and their status are monitored.
root@omer:~# hping3 -S 192.168.254.130 -c 3 HPING 192.168.254.130 (eth0 192.168.254.130): S set, 40 headers + 0 data bytes len=46 ip=192.168.254.130 ttl=64 DF id=0 sport=0 flags=RA seq=0 win=0 rtt=8.2 ms len=46 ip=192.168.254.130 ttl=64 DF id=0 sport=0 flags=RA seq=1 win=0 rtt=7.4 ms len=46 ip=192.168.254.130 ttl=64 DF id=0 sport=0 flags=RA seq=2 win=0 rtt=4.4 ms --- 192.168.254.130 hping statistic --- 3 packets transmitted, 3 packets received, 0% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 4.4/6.7/8.2 ms root@omer:~#

The output of the packages with the tcpdump command is as follows.
root@omer:~# tcpdump -i eth0 -c 3 -nn -vv host 192.168.254.130
tcpdump: listening on eth0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes
13:57:42.373129 IP (tos 0x0, ttl 64, id 17592, offset 0, flags [none], proto TCP (6), length 40)
192.168.254.129.2272 > 192.168.254.130.0: Flags [S], cksum 0xac8f (correct), seq 343423179, win 512, length 0
13:57:42.373546 IP (tos 0x0, ttl 64, id 0, offset 0, flags [DF], proto TCP (6), length 40)
192.168.254.130.0 > 192.168.254.129.2272: Flags [R.], cksum 0xdb56 (correct), seq 0, ack 343423180, win 0, length 0
13:57:43.241008 ARP, Ethernet (len 6), IPv4 (len 4), Request who-has 192.168.254.2 tell 192.168.254.130, length 46
3 packets captured
4 packets received by filter
0 packets dropped by kernel