In Linux systems, “chmod” command is used to determine the access rights of users to files. It allows us to change the access permissions of the files we specify. The exact equivalent of chmod is change mode.
When we examine the example below; We can sort it as a user, group and other from left to right, which comes in 3 blocks after the first character. Access permissions are always given in the form of rwx. If there is a “-” sign instead of rwx, it means that the permission is not allowed in the place coming to that section. Linux Users There are 3 user types. These;
(Type) | (user) | (group) | (other)
– | – – – | – – – | – – –
omer@omer:~/Downloads$ ls -all total 70764 drwxr-xr-x 2 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 12:23 . drwxr-xr-x 15 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 12:25 .. -rw-r--r-- 1 omer omer 72446160 Dec 8 12:23 google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb

u – user (file or directory owner, creator)
g – group (the group to which the file or directory belongs)
o – other (other than user and group)
a – all (user, group, other) (all, anyone can access files and directories.)
How can I view the chmod permissions?
You can use the “ls -all” command to see the chmod permissions on a directory or file. File operations are divided into reading, write and execute.
r – Read permission: Authorization to read the file. This privilege also has the ability to list all files in that directory when given for a directory.
w – Write permission: Authorization to create, change or delete a file.
x – Execute permission: Many users can read many files on Linux systems. However, it must also have the authorization to run it.
Note: Only the owner or a more authorized user can change the authority of a file.
File types
The first character indicates the type of file. We can list the types of file as follows.
omer@omer:~/Downloads$ ls -all total 70764 drwxr-xr-x 2 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 12:23 . drwxr-xr-x 15 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 12:25 .. -rw-r--r-- 1 omer omer 72446160 Dec 8 12:23 google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb

– : A normal file
d : Directory
b : Custom block file
c : Special character file
l : Symbolic link file
P : Specially named pipe file
Chmod Permissions with Numbers
Chmod permissions can be either letters or numbers.
000: r (No right to read), w (No write right), x (No right to work):
—: chmod value is 0
001: r (No right to read), w (No write right), x (Right to work)
– -x: chmod value 1
010: r (No right to read), w (Write right), x (No work right)
-w-: chmod value 2
011: r (No right to read), w (Write right), x (Right to work)
-wx: chmod value 3
100: r (Read right), w (No write right), x (No work right)
r- -: chmod value 4
101: r (Right to read), w (No write right), x (Right to work)
r-x: chmod value 5
110: r (Read right), w (Write right), x (No work right)
rw-: chmod value 6
111: r (have the right to read), w (have the right to write), x (have the right to work)
rwx: chmod value 7
Chmod Operators
You can see the Operators for chmod permissions as follows.
– : remove chmod permission.
+ : add chmod permission.
= : set chmod permission.
Note: The file owner, parent and root user can change the chmod access permission of a file and directory.
Some examples of chmod
rwx: Read, write and run access permissions are all available.
rw-: Read and write permissions, no permission to run.
r-x: Read and run permissions, no permission to write.
-wx: No permission to reading, write and run permissions.
r–: Only has the right to read.
-w-: It only has the right to write.
–x: Only have the right to run.
—: No access rights.
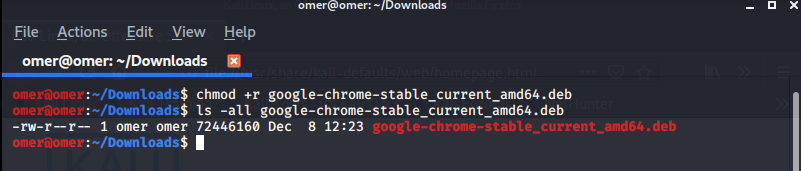
Example 1: “chmod +r” Command
chmod +r filename: We have given read permission to the file.
omer@omer:~/Downloads$ chmod +r google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb omer@omer:~/Downloads$ ls -all google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb -rw-r--r-- 1 omer omer 72446160 Dec 8 12:23 google-chro
Example 2: “chmod u=rw,go=” Command
chmod u=rw,go= filename: We gave read and write permission to the file owner. We removed all access permissions for the group and others.
omer@omer:~/Downloads$ chmod u=rw,go= google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb omer@omer:~/Downloads$ ls -all google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb -rw------- 1 omer omer 72446160 Dec 8 12:23 google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb

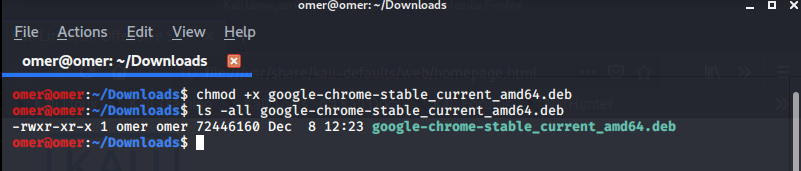
Example 3: “chmod +x” Command
chmod +x filename: We gave the file run permission for all users (user, group, other).
omer@omer:~/Downloads$ chmod +x google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb omer@omer:~/Downloads$ ls -all google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb -rwx--x--x 1 omer omer 72446160 Dec 8 12:23 google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb
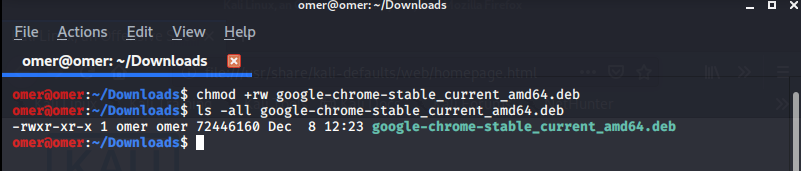
Example 4: “chmod +rw” Command
chmod +rw filename: We have given read and write permissions for the user issuing the command, read-only permissions for the group and others.
omer@omer:~/Downloads$ chmod +rw google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb omer@omer:~/Downloads$ ls -all google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb -rwxr-xr-x 1 omer omer 72446160 Dec 8 12:23 google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb
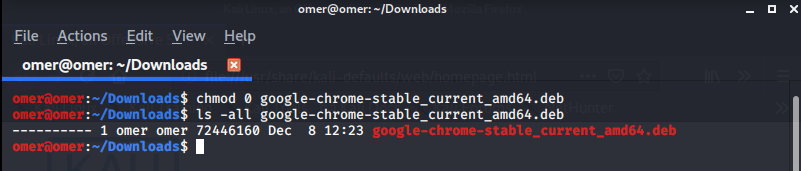
Example 5: “chmod 0” Command
chmod 0 filename: We removed all users access permissions for the file.
omer@omer:~/Downloads$ chmod 0 google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb omer@omer:~/Downloads$ ls -all google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb ---------- 1 omer omer 72446160 Dec 8 12:23 goog
Example 6: “chmod 666” Command
chmod 666 filename: We have given read and write permissions for all users.
omer@omer:~/Downloads$ chmod 666 google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb omer@omer:~/Downloads$ ls -all google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb -rw-rw-rw- 1 omer omer 72446160 Dec 8 12:23 google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb

Example 7: “chmod 0755 or chmod 755” Commands
chmod 0755 or chmod 755 filename: It doesn’t matter if this command is written in two different ways. His task is the same. It gives read, writes and execute rights to the file owner and read and execute rights for the group and others.
omer@omer:~/Downloads$ chmod 755 google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb omer@omer:~/Downloads$ ls -all google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb -rwxr-xr-x 1 omer omer 72446160 Dec 8 12:23 google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb

Example 8: “chmod ugo-rwx” Command
chmod ugo-rwx filename: We have removed all access permissions for the file. chmod 0 or chmod 000 do the same.
omer@omer:~/Downloads$ chmod ugo-rwx google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb omer@omer:~/Downloads$ ls -all google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb ---------- 1 omer omer 72446160 Dec 8 12:23 google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb

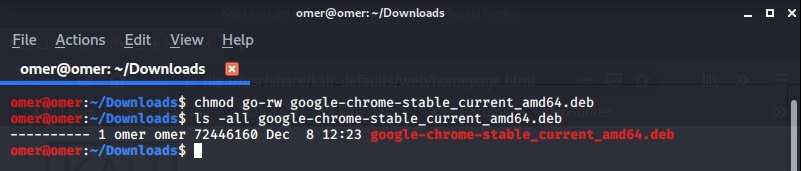
Example 9: “chmod go-rw” Command
chmod go-rw filename: We removed the read and write rights of the group and other users on the file.
omer@omer:~/Downloads$ chmod go-rw google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb omer@omer:~/Downloads$ ls -all google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb ---------- 1 omer omer 72446160 Dec 8 12:23 google-chrome-stable_curr
Example 10: “chmod –R u + r” Command
chmod –R u + r Download: We have given read permission to its user for all files and directories under the directory named Download. With the -R (recursive) parameter, the chmod access permission of all files and directories under the relevant directory is changed in the same way.
r:~$ chmod -R u+r Downloads/ omer@omer:~$ ls -all Downloads/ total 70764 drwxr-xr-x 2 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 12:23 . drwxr-xr-x 15 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 12:25 .. -r-------- 1 omer omer 72446160 Dec 8 12:23 google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb omer@omer:~$

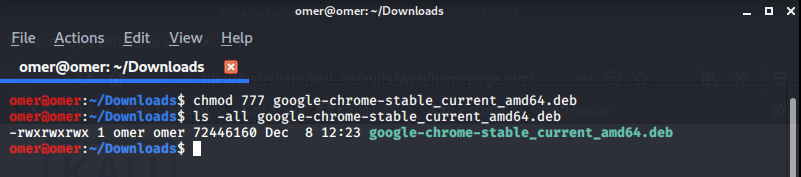
Example 11: “chmod a + rwx and chmod 777” Commands
chmod a + rwx and chmod 777 filename: Two different commands but the same functions. It ensures that all users have read, write and run rights on the relevant file.
omer@omer:~/Downloads$ chmod 777 google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb omer@omer:~/Downloads$ ls -all google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb -rwxrwxrwx 1 omer omer 72446160 Dec 8 12:23 google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb
Example 12: “chmod go + r” Command
chmod go + r filename *: (*) gives permission to read all files that start with the trial with wildcard parameter by the group and other (other) users.
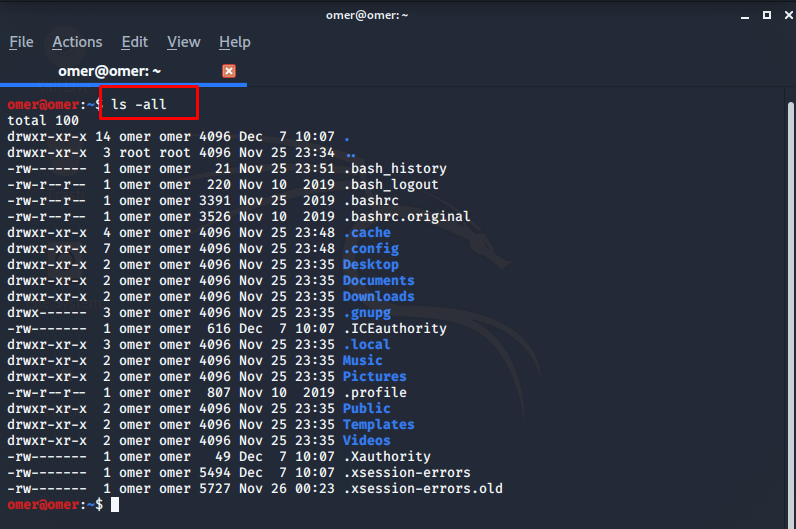
omer@omer:~/Downloads$ ls -all total 70772 drwxr-xr-x 4 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 16:01 . drwxr-xr-x 15 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 12:25 .. -rwxrwxrwx 1 omer omer 72446160 Dec 8 12:23 google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb d--------- 2 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 15:55 test1 d--------- 2 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 16:02 test2 omer@omer:~/Downloads$ chmod go+r test* omer@omer:~/Downloads$ ls -all total 70772 drwxr-xr-x 4 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 16:01 . drwxr-xr-x 15 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 12:25 .. -rwxrwxrwx 1 omer omer 72446160 Dec 8 12:23 google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb d---r--r-- 2 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 15:55 test1 d---r--r-- 2 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 16:02 test2
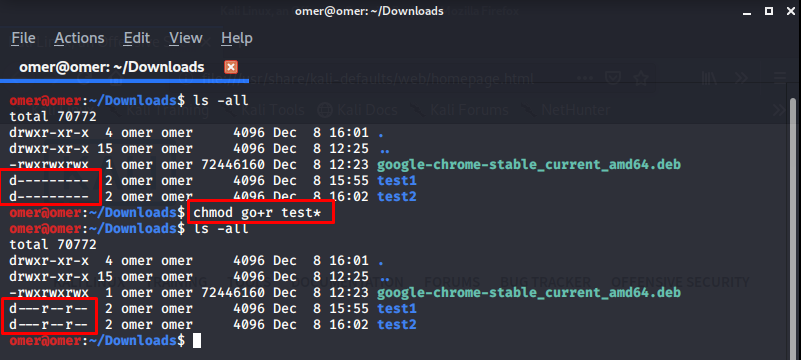
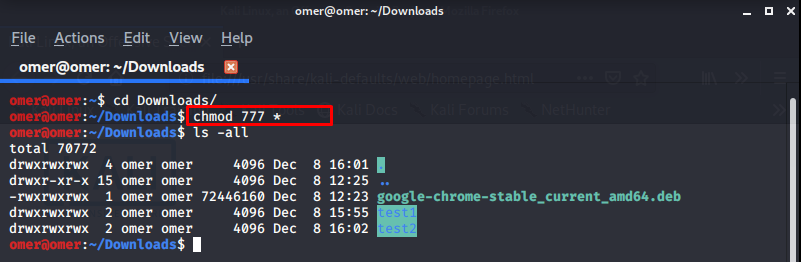
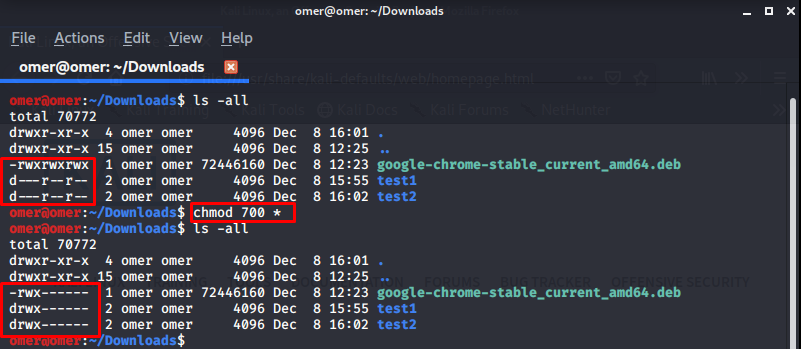
Example 13: “chmod go-rwx * or chmod 700 *” Commands
chmod go-rwx * or chmod 700 *: Used when inside a directory. Read, write and run access permissions for the group and other users are removed from all files and subdirectories in the directory where it is used.
omer@omer:~/Downloads$ ls -all total 70772 drwxr-xr-x 4 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 16:01 . drwxr-xr-x 15 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 12:25 .. -rwxrwxrwx 1 omer omer 72446160 Dec 8 12:23 google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb d---r--r-- 2 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 15:55 test1 d---r--r-- 2 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 16:02 test2 omer@omer:~/Downloads$ chmod 700 * omer@omer:~/Downloads$ ls -all total 70772 drwxr-xr-x 4 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 16:01 . drwxr-xr-x 15 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 12:25 .. -rwx------ 1 omer omer 72446160 Dec 8 12:23 google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb drwx------ 2 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 15:55 test1 drwx------ 2 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 16:02 test2
Example 14: “chmod u = rw, go =” Command
chmod u = rw, go = filename: This example, we removed the user’s right to run, reserving the read and write rights. We have also removed run, write and read rights in group and others.
omer@omer:~/Downloads$ ls -all test1 total 12 drwxrwxrwx 2 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 15:55 . drwxr-xr-x 4 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 16:01 .. -rw-r--r-- 1 omer omer 45 Dec 8 15:55 pentest1.txt omer@omer:~/Downloads$ chmod u=rw,go= test1 omer@omer:~/Downloads$ ls -all test1 ls: cannot access 'test1/..': Permission denied ls: cannot access 'test1/pentest1.txt': Permission denied ls: cannot access 'test1/.': Permission denied total 0 d????????? ? ? ? ? ? . d????????? ? ? ? ? ? .. -????????? ? ? ? ? ? pentest1.txt omer@omer:~/Downloads$ cd test1 bash: cd: test1: Permission denied

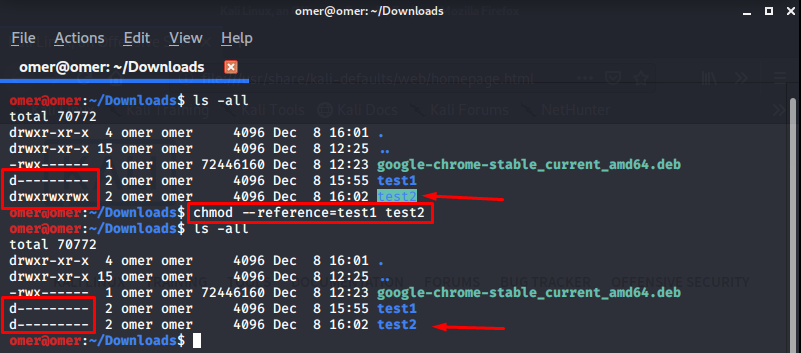
Example 14: “chmod –reference=file_x file_y” Command
chmod –reference=file_x file_y: Lastly, it is a useful parameter that we use a lot. It also applies the permissions of file_x to file_y.
omer@omer:~/Downloads$ ls -all total 70772 drwxr-xr-x 4 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 16:01 . drwxr-xr-x 15 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 12:25 .. -rwx------ 1 omer omer 72446160 Dec 8 12:23 google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb d--------- 2 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 15:55 test1 drwxrwxrwx 2 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 16:02 test2 omer@omer:~/Downloads$ chmod --reference=test1 test2 omer@omer:~/Downloads$ ls -all total 70772 drwxr-xr-x 4 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 16:01 . drwxr-xr-x 15 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 12:25 .. -rwx------ 1 omer omer 72446160 Dec 8 12:23 google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb d--------- 2 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 15:55 test1 d--------- 2 omer omer 4096 Dec 8 16:02 test2
Umask
Returns the system default file creation mask value. The default value of umask is 0002. The first character of this value makes no sense. Other characters indicate the file permission according to the base octal.
umask u = rw, go =
This definition indicates that, by default, the files opened in the system are read and write for the user, and group and other users are unauthorized.
Note: Files created using the sudo command are owned by root and access to the file belongs only to root privileges.




