PfSense is a FreeBSD based Firewall distribution. It is open to development as it has free and open-source codes. Pfsense firewall has low system requirements. You can use this distribution very easily with a 1 GB disk capacity and 128 MB memory. After installation, configuration processes are done from the web interface prepared for Pfsense. In addition to being a powerful and flexible firewall and router platform, it has the advantage of having a long list of features and a package system. This package system not only gives the operating system easy expansion flexibility but also prevents security vulnerabilities in distribution. You can install it in small networks consisting of a single computer, in large enterprises with thousands of network devices.
What can be done with Pfsense Firewall?
- You can restrict or block the pages that users on your network can access. You can make time restrictions. You can block any apps you want.
- You can record the pages visited by your users with a detailed date stamp.
- You can restrict by specifying categories. (For example; Game sites, Forums, download sites, sites with pornographic content, etc.).
- Restrictions can be made by dividing users into groups (For example, students, teachers, staff, accounting, etc.).
- Users can be allowed to access the internet with the specified username and password information. So no one can access the internet even if your wifi network is not password protected.

System requirements of Pfsense
Despite this many features, Pfsense has low system requirements for system requirements.
Pfsense minimum system requirements are;
- Processor: 100Mhz Intel Pentium +
- Memory: 128MB+
- Disk: 1GB+
- PfSense ISO file
Pfsense Technical Specifications
The firewall
- Filtering by Source or Destination IP, Protocol, UDP/TCP traffic to source or destination port.
- Ability to restrict connections based on rules.
- Allowing or blocking the passage of packets according to the operating system.
- Keeping or not keeping records for each rule.
- Policy-based routing for each rule. Especially like load balancing, failover, multi-wide network connection management.
- Grouping of IP, network or ports using Alias system.
- Ability to implement transparent layer 2 firewalls.
- Packet normalization.
Captive Portal
- Captive Portal service is a service that allows users to be authorized or to switch to a page by clicking on a page to receive network service. This service can be used especially in wireless public areas, as well as incorporate networks to provide an extra layer of security to wireless networks.

State Table
- The default state table size is 10000 states, but this can be changed as needed.
- Allows connections to be terminated in a shorter time.
- The number of Client Connections can be restricted.
- The number of connections to the target server can be restricted.
- The number of connections that can be opened per second can be restricted.
- Status timeout values can be set.
- State type can be set (keep state, modulate state, synproxy).
- It tries to keep legal connections in longer-term memory.
Load Balancing
- Allows multiple wide-area network connections to be used in local networks and prevents exit from trouble lines by performing error checking.
- It allows more than one server to provide the same service as a single server. Servers that do not respond to ping packets are automatically removed from the service pool.
- VPN PfSense offers three options for VPN. These; IPSec, OpenVPN, L2TP.

Freeradius
- Freeradius is a free and open-source radius software. It enables the application of radius on PfSense.
Lightsquid
- LightSquid allows URL records produced by squid to be viewed as an html page and based on IP/Host/URL.
DHCP Server and Dhcp Transfer(Relay)
- PfSense can be set up as a dhcp server or as a server to transfer dhcp requests.

DNS Server
- PfSense ensures that DNS servers are kept on their own and their services are provided.
Siproxd
- Siproxd is a proxy masking server for the SIP protocol. It enables the handling of SIP clients in private IP networks and the appropriate rewriting of SIP message headers for Address Translation (NAT) and subsequent connection.
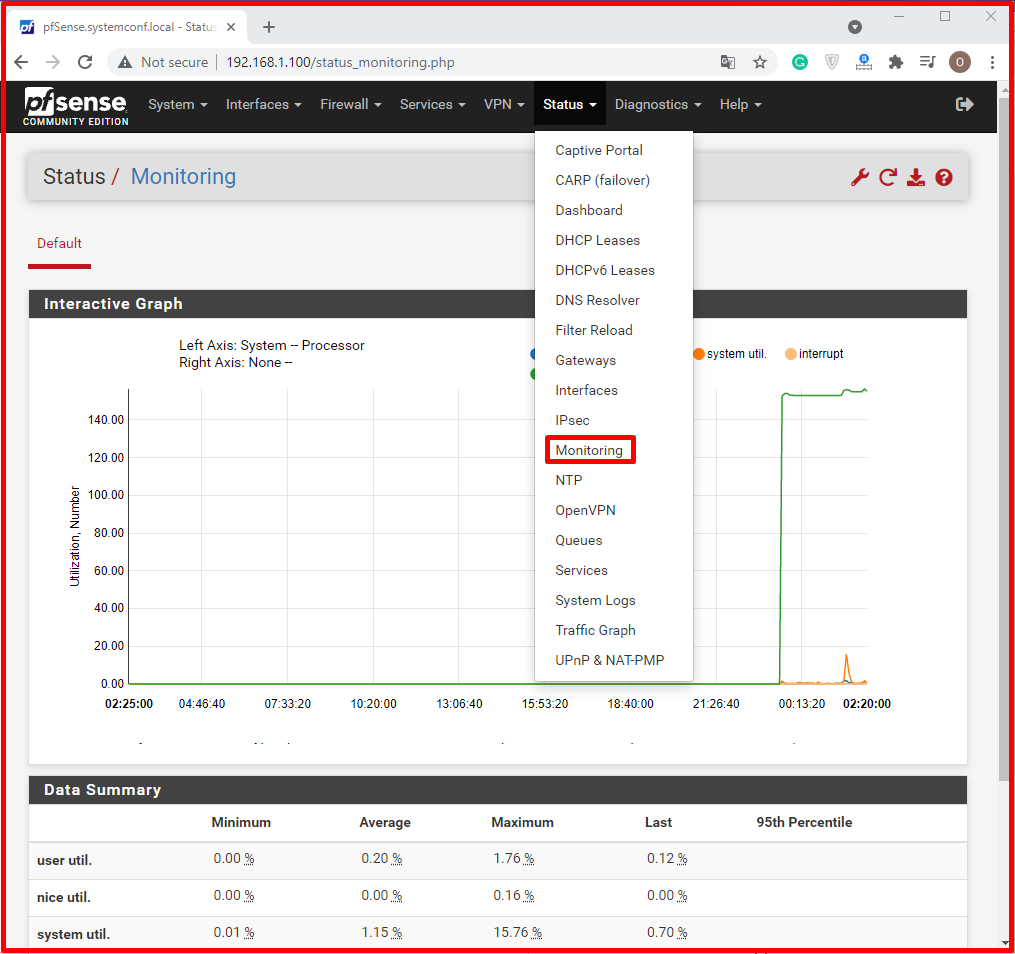
Reporting and Monitoring
RRD charts provide the following information, retrospectively.
- CPU usage.
- Total throughput.
- Firewall status table.
- Separate throughput values for each interface.
- The amount of traffic passing per second for each interface separately.
- Ping access times from wide area network interface (WAN) gateways.
- Queuing graphics in traffic shaping systems.
- Real-Time Information.
- SVG graphics display traffic passing through interfaces in real-time.