McAfee’s Threat Prevention product is known as McAfee antivirus. McAfee Threat Prevention generally monitors behaviour/access-based, reputation-based, signature-based, random code studies and takes action according to policy. The following policies are explained in the following features as the McAfee Threat Prevention policy. There are four modules in McAfee’s “Endpoint Security Threat Prevention“. These;
- On-Access Scan
- On-Demand Scan
- Access Protection
- Exploit Prevention
On-Access Scan
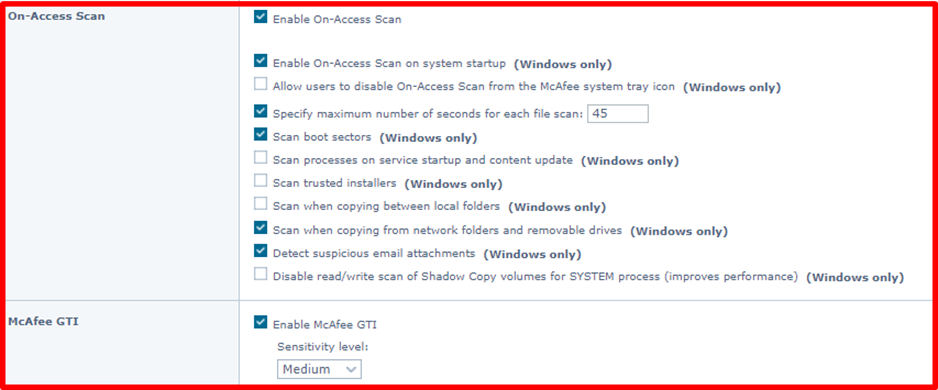
“On-Access Scan” provides continuous, real-time threat detection by inspecting files as the user accesses them. It integrates with the system at the lowest levels and scans files where they first enter the system. When detections occur, it sends notifications to the service interface.
On-Demand Scan
The “On-Demand Scan” module scans files, folders, memory and registry, looking for malware that may have infected the computer. It is possible to decide when and how often to perform on-demand scans. Systems can be scanned manually or at a scheduled time.

Access Protection
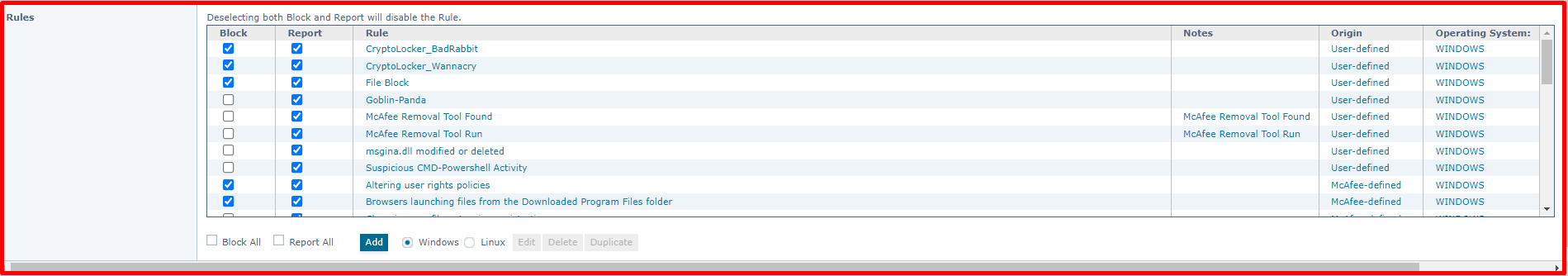
The Access Protection module allows defining access control policies and settings for processes, files, and directories. It protects the system from security vulnerabilities by restricting access to certain files and directories. You can create new Access Protection rules, edit rule settings or delete rules from the command line. The action for each rule can be defined as Report, Block or Block and Report. There are 32 rules in total in the Access Protection policy by default.
Exploit Prevention
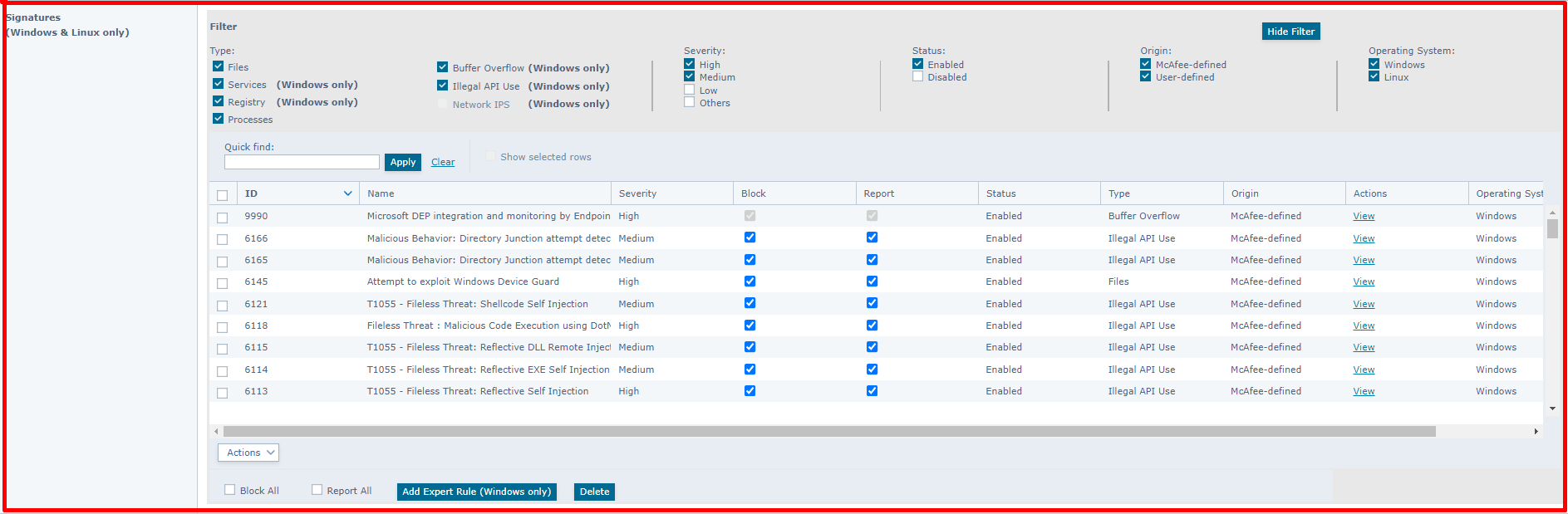
It prevents unwanted changes to the client system by restricting access to files, shares, registry keys, registry values, processes and services. It prevents applications from running arbitrary code. Detects and prevents known network-based attacks. There are 355 signatures in total. 175 of them are active. Since activating all signatures will create false-positive, signatures that should be active due to the structure of the institution can be opened.
What is McAfee Adaptive Threat Protection?
Adaptive Threat Protection uses rules to determine what actions to take based on multiple data points such as reputations, local intelligence, and contextual information. Adaptive Threat Protection performs real-time scanning. Adaptive Threat Protection works differently depending on whether it communicates with the TIE(Threat Intelligence Exchange).
- If a TIE server is available, Adaptive Threat Protection uses the Data Exchange Layer (DXL) framework to instantly share file and threat information across the enterprise. It can see where a threat was first detected, where it went from there, and stop the particular system.
- Adaptive Threat Protection allows checking file reputation at the local level in the environment with the TIE server. It is decided which files can run and which to block, and the Data Exchange Layer (DXL) instantly shares the information with clients.
- If there is no TIE server and the system is connected to the Internet, Adaptive Threat Protection uses McAfee GTI(Global Threat Intelligence) for reputation decisions.
- If there is no TIE server and the system is not connected to the Internet, Adaptive Threat Protection uses information about the local system to determine file reputation.