It is a policy and procedure framework created to provide secure authentication for a business’s digital assets. IT departments use IAM software to securely control users’ access privileges and applications across on-premises and cloud-based systems.
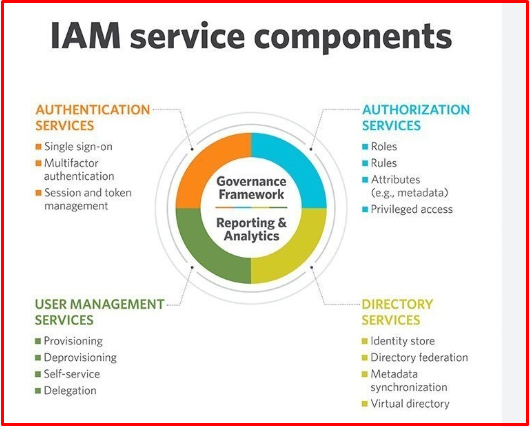
IT teams implement the IAM framework using identity and access management software, which typically comes with features such as single sign-on (SSO), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and privileged access management (PAM). This software centralizes identity management, controls access to digital assets, detects anomalies in user behaviour, and informs IT and security teams about potential risks.
Businesses can deploy IAM systems with on-premises or cloud-based IAM to secure user identities for employees, partners, and remote users. These systems help businesses concentrate multiple user identities into a single digital identity held under a central system. This provides access to all applications from a central location and reduces clutter. You can infer which applications a user has authority in the company and to which authority they belong.
IAM System Steps
A basic IAM system follows two steps. These are:
Authentication: Users enter their credentials, and IAM systems verify the username and password against the credentials stored in the database. Users may need to prove their identity more than once and pass multiple authentication checks to gain access.
Authorization: Based on the user identity and role in the business, IAM systems assign them the appropriate privileges they need to conduct their business. For example, IAM allows an editor to make changes, but blocks administrative privileges such as adding or deleting user accounts.
What is identity governance?
Identity governance provides solutions for access management and directory services. Identity governance helps organizations strengthen security, simplify compliance, and capture business opportunities related to mobile access and social media identity access.
What is identity governance?
It manages the provisioning and deprovisioning of users and provides actionable credentials that enable rapid remediation of high-risk user entitlements. Self-service features allow users to initiate application onboarding processes for on-premises and cloud applications using Rest APIs and various connectors. Identity governance allows users to flexibly aggregate their existing identities, associated entitlements, and roles for faster onboarding. Compliance processes are accelerated with certifications based on time, activity, or organization. Assessments focus on high-risk entitlements or compliance-based objectives (for example, GDPR). Identity governance continuously scans the business to identify and remediate policies that impact segregation of duties.
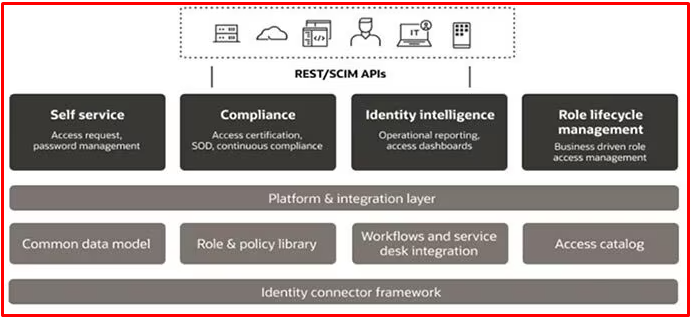
Differences Between Identity Management and Access Management
While identity management and access management are related, they are not the same. While identity management is about authentication, access management is about authorization. For example, identity management forces a user to authenticate, and then based on the user’s identity and role, access management decides whether they have permission to access information.
| Features | IAM | PAM |
| Users and IT Assets | After deployment, IAM helps businesses control and manage both users and IT assets simultaneously. | PAM helps IT administrators secure access to IT assets at a granular level and prevents unauthorized users from misusing information assets. |
| Reliability & Resiliency | The demand for IAM is largely due to its flexibility to deploy with any of the business’ existing platforms; The flexibility of IAM can easily be exploited to create security risks. | PAM is comparatively less adaptable than IAM. It bridges the gap between flexibility and security and enforces strict access control policies for business-critical assets. |
| Provisioning and Deprovisioning | IAM helps provision and deprovision all end users to access applications. | PAM, on the other hand, allows only privileged users to access critical systems and applications only after verifying the authenticity of the users. |




