In Linux-based operating systems, information about network operations such as network settings, network commands or network configuration is included. In Linux operating systems, as everything is a file, network settings are also kept in files. The settings can be edited with any text editor or by various tools.
Network files
Network settings are located in the following files and directories.
/ etc / sysconfig / network file / etc / sysconfig / network-scripts directory / etc / hosts /etc/resolv.conf /etc/nsswitch.conf / etc / services
Each of the settings files is used for different operations. The files in the network-scripts directory are used for network settings. Network settings are eth0, eth1, etc. according to the network card in files starting with ifcfg. kept by names.
Inside the network settings;
DEVICE - Name of the network card. ONBOOT - The state that the network is activated at startup. BOOTPROTO - How to set network settings (static, dhcp, bootp). IPADDR - IP address. NETMASK - Network mask. BROADCAST - Broadcast address. GATEWAY - Specifies the gateway address.
It also has various settings such as MAC address, Network type. When you want to get IP using DHCP, it will be sufficient to write the DEVICE, BOOTPROTO and ONBOOT settings.
Network Operations
In Linux systems, we can use the following commands to examine the Stop, Start, Restart and Status of our Network services.
Stop Network Service
You can stop the network service as follows. Check before stopping the service. There will be a problem with your connection. We recommend that you try it in your test environment.
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
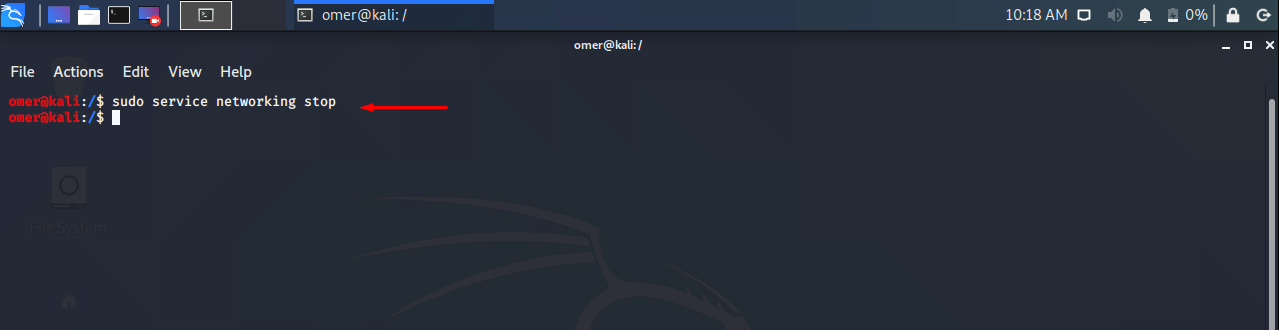
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint etc. We will use the networking stop command to service networking stop.
sudo service networking stop
Fedora and CentOS
Fedora and CentOS etc. We will use the networking stop command to systemctl stop network.target.
systemctl stop network.target

Start Network Service
You can start the network service as follows.
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
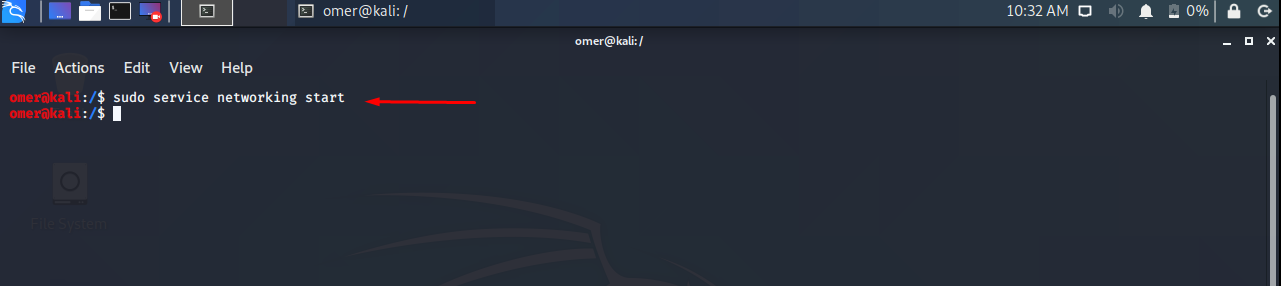
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint etc. We will use the networking start command to sudo service networking start.
sudo systemctl start NetworkManager-dispatcher.service
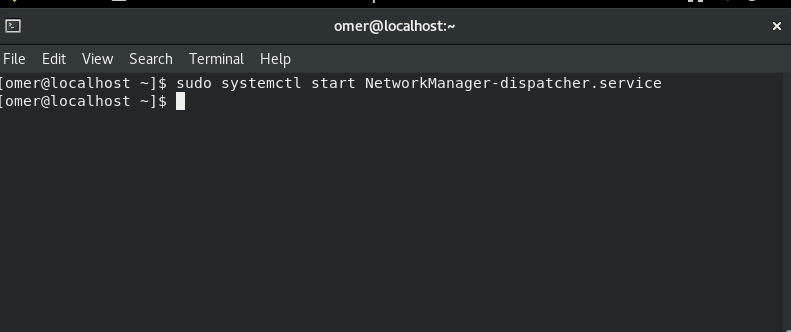
Fedora and CentOS
Fedora and CentOS etc. We will use the networking stop command to sudo systemctl start NetworkManager-dispatcher.service.
sudo systemctl start NetworkManager-dispatcher.service
Status Network Service
You can status the network service as follows.
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
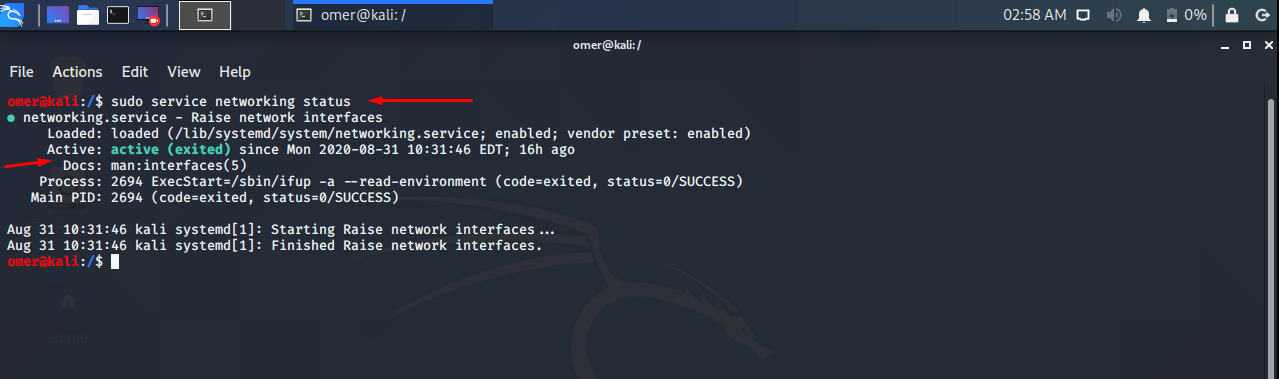
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint etc. We will use the networking start command to sudo service networking status.
sudo service networking status
Fedora and CentOS
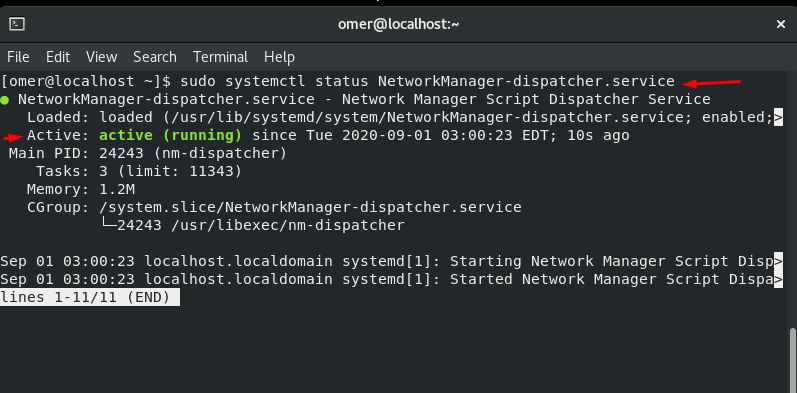
Fedora and CentOS etc. We will use the networking stop command to sudo systemctl status NetworkManager-dispatcher.service.
sudo systemctl status NetworkManager-dispatcher.service
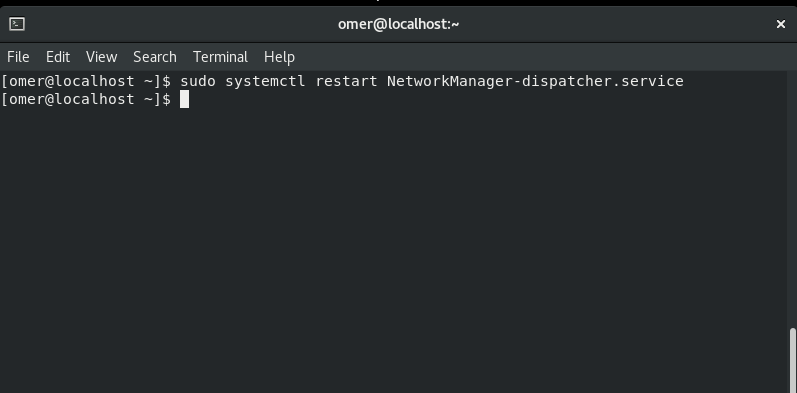
Restart Network
You can restart the network service as follows.
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali and Mint
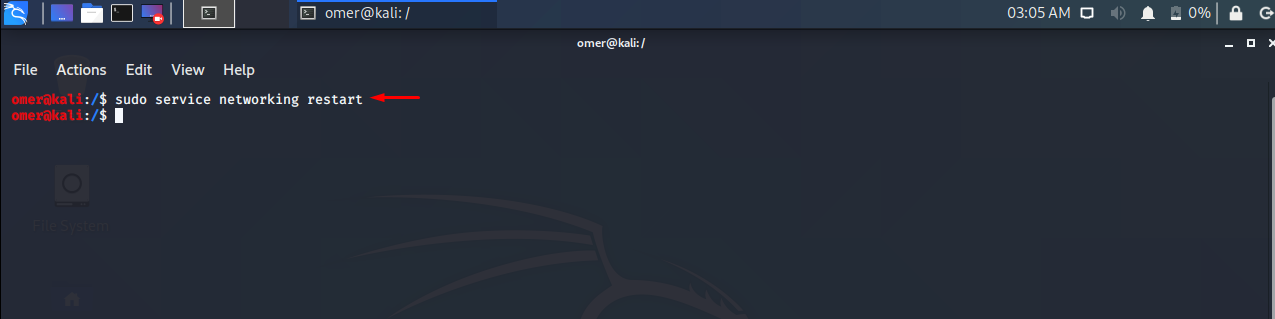
Ubuntu, Debian, Kali, Mint etc. We will use the networking start command to sudo service networking restart.
sudo service networking restart
Fedora and CentOS
Fedora and CentOS etc. We will use the networking stop command to sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager-dispatcher.service.
sudo systemctl restart NetworkManager-dispatcher.service