We will see the steps we need to check when we have a problem with the ip in our Centos operating system.
First step
First of all, we check with the “systemctl status NetworkManager.service” command to find out the status of the Network service.
sudo systemctl status NetworkManager.service

Then we view the network unit running in Centos with the “nmcli dev status” command. As you can see, the Network Manager service is active. Ens33 also appears as the network unit.
Note: The network unit name does not have to be ens33. It may differ.
nmcli dev status

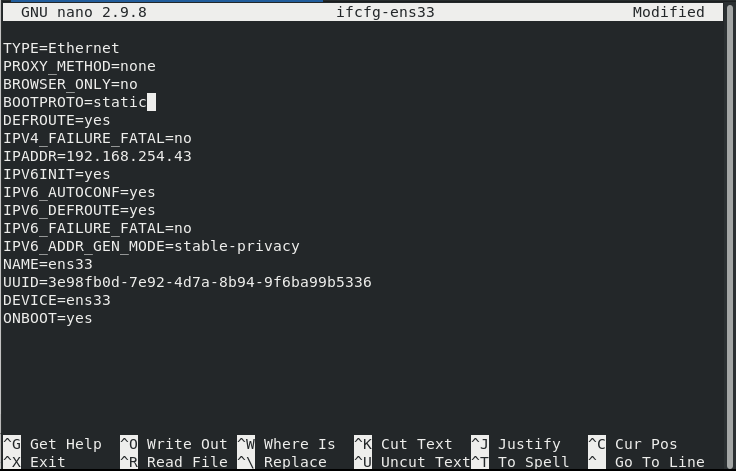
We proceed to the process of configuring the ens33 network unit. For this, we go to the “/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts” location. With the “nano” command, we enter the unit “ifcfg-enp0S3“.
nano ifcfg-ens33

The steps we need to pay attention to in the network config file:
- IPADDR=192.168.x.x – You need to give a free ip address on your network.
- ONBOOT=yes –The option allows it to automatically detect the network when the server is restarted.
TYPE=Ethernet PROXY_METHOD=none BROWSER_ONLY=no BOOTPROTO=static DEFROUTE=yes IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPADDR=192.168.254.43 IPV6INIT=yes IPV6_AUTOCONF=yes IPV6_DEFROUTE=yes IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6_ADDR_GEN_MODE=stable-privacy NAME=ens33 UUID=3e98fb0d-7e92-4d7a-8b94-9f6ba99b5336 DEVICE=ens33 ONBOOT=yes
After entering the settings, we save and exit and restart the network service with the “systemctl restart network.service” command. After the network service is restarted, you can check if it gets ip with “ifconfig” or “ip addr” commands.
systemctl restart network.service
Second step
As a second step, we click on the “Activities” menu on the top left and click on “Settings“.

We click on the “Network” tab on the “Settings” page. Click on the settings in the “Wired” section on the side.

We click on the “IPv4” tab on the “Wired” page. We click on the “Manual” tab at the bottom. Here, we can manually give the ip address we want. Here we have configured the Static IP address.





